Most Popular
-
Bulletproof Glass Industry Trends
Bulletproof Glass Industry Trends,s indicated by a market report distributed by Persistence Market R.. -
Areas of Revolution in Urban Mobility
It promises to be the most far-reaching advance in mobility since the invention of the automobile it.. -
Industrial IoT, The agent of change for Defense system
The Internet of Things (IoT) is today's business push to incorporate a wide assortment of specialize.. -
Imperatives of Big Data Analytics in Defence
Defence and Security related data being generated from numerous sources should be completely dissect.. -
IoT: Game - changer for Aviation Industry
Internet of Things(IoT) has taken its place everywhere now. It is in which the everyday objects/thin.. -
Airlines need to fund Pilot training
A move far from the compensation to-fly plan and back towards the model of bearers paying for prepar..
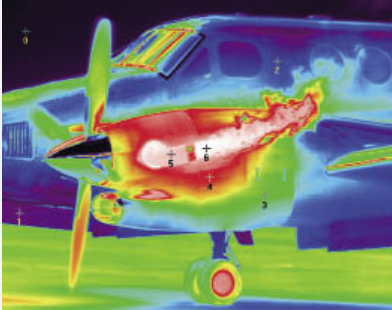
Infrared thermography (IRT) emerges as a powerful tool, providing a non-destructive way to assess the health and functionality of various components. IRT utilizes infrared radiation, invisible to the naked eye, to create a thermal image. This image represents the temperature distribution on a surface, allowing for identification of hot and cold spots. Between 2023 and 2032, the infrared thermography market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of more than 5.5%, from a projected valuation of over USD 400 million in 2022. Because NDT techniques can quickly and accurately assess the state of materials and equipment without causing damage, their growing use is propelling the market's expansion.
Applications in Aerospace:
- Composite Material Inspection: IRT shines a light on hidden defects within composite materials used in aircraft structures. It can reveal delaminations (separations between layers), voids (air pockets), and cracks, even if they lie beneath the surface. Early detection of these weaknesses prevents potential catastrophic failures during flight.
- Honeycomb Inspections: Honeycomb structures, known for their lightweight properties, are commonly used in wings and fuselage panels. IRT helps identify moisture trapped within the honeycomb core, which can compromise its structural integrity. Early detection allows for repairs before the damage worsens.
- Bonding Inspection: Strong bonding is crucial for various aircraft components. IRT reveals inconsistencies in bonding between different materials, ensuring a secure and reliable connection.
- Overheated Components: IRT readily identifies components experiencing overheating, which could be a sign of potential malfunctions or imminent failures. This allows for targeted maintenance and prevents in-flight emergencies.
- Electrical System Inspection: Overheated electrical components pose a significant safety risk. IRT helps identify these issues, enabling preventative maintenance and reducing the risk of electrical fires.
- Tribology (Friction & Wear): IRT can monitor wear and tear on critical components like bearings and landing gear. Early detection allows for timely lubrication or replacement, preventing breakdowns and ensuring optimal performance.
Advantages of IRT in Aerospace:
- Non-destructive: IRT doesn't require any physical contact with the aircraft components, ensuring no damage during inspection.
- Rapid inspection: IRT scans are quick and efficient, minimizing downtime for aircraft.
- Cost-effective: IRT inspections can be performed regularly and preventatively, avoiding costly repairs later.
- Remote monitoring: Thermal cameras can be used for remote inspections, reducing the need for personnel to access difficult-to-reach areas.
- Early detection: IRT detects issues before they become major problems, preventing accidents and ensuring safety.
Overall, infrared thermography is an invaluable tool in the aerospace industry. Its ability to detect problems early, assess component functionality, and facilitate predictive maintenance contributes significantly to ensuring the safety, reliability, and performance of aircraft. As technology advances, IRT applications within the aerospace industry are likely to become even more sophisticated and widespread.